Beyond the Job
To become more agile and to accommodate changing worker demands, organizations will increasingly do away with the traditional concept of the job. As a result, organizations need a fundamental rethink of the operating model for talent and work.

Ever since Adam Smith wrote about the division of labor over a century ago, jobs have been the dominating structure for organizing work. Managers give feedback, hire, promote and organize their teams around people in “jobs.” As HR professionals, our function has been based on the concept of the “job” with a fixed set of responsibilities. We write job descriptions, set compensation levels, create organizational charts, assign training and manage performance—all around these pre-defined jobs.
But the very notion of the job is increasingly becoming a relic of the industrial era. This approach worked well when organizations were stable and predictable, and when organizations competed more on scalable efficiency than on speed, innovation and agility.
If there’s a single thread running through the narratives on future of work, it is that we are moving away from the mechanistic, industrial models of the past to a more fluid, human and digital future in which our organizations, people and work organically adapt in real-time—and one with an ever-expanding portfolio of stakeholders, workforces, work options, work places and strategic futures that can no longer be categorized into simple boxes. To adapt to a changing world, we need to build something far more fit for purpose in a world in which speed, agility and innovation rule the day, and in which people expect more meaning, choice, growth and autonomy at work.
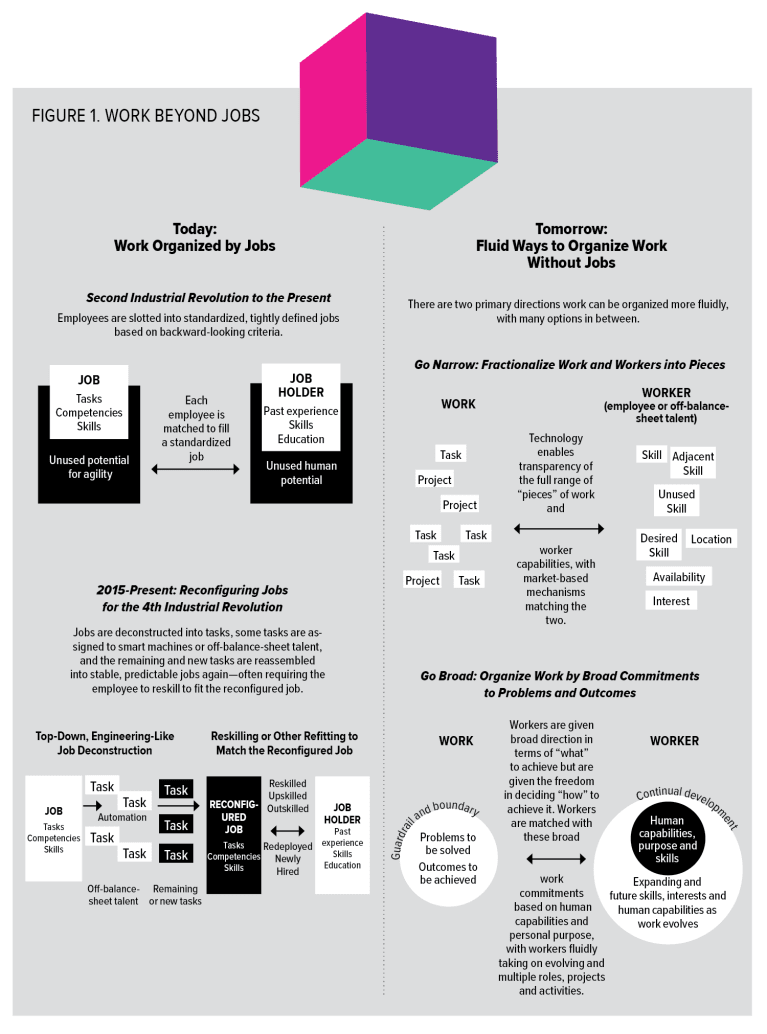
In recent years, thinking on the future of work has focused on the need to reconfigure jobs—not to reimagine or replace them entirely. The reasoning goes like this: As alternative approaches to work have emerged such as artificial intelligence (AI), automation and off-balance-sheet talent, we need to disaggregate the job into component tasks, determine which tasks can be performed more optimally by smart machines or alternative talent outside of the organization’s walls, and then reassemble the remaining tasks with new ones to create a newly reconfigured job. Employees are then reskilled, upskilled or outskilled to once again meet the needs of the newly reconfigured job, with automation either substituting for, augmenting or transforming the human worker’s role (see Figure 1).
But this approach is a top-down, engineering-like approach still rooted in a mechanistic mindset that doesn’t give workers much choice or agency. Too often, the focus is on chasing efficiency and cost reduction instead of opening up new opportunities to unlock growth and value. And the world is simply changing too fast to go through this process again and again each time a new technology emerges, markets shift or new opportunities emerge.
If anything has shown the need for greater agility, it has been the pandemic. Forced to become more agile, organizations fluidly moved people to where the work was; created agile, cross-functional SWAT teams to tackle complex problems; and experimented with new work models. For many of us, the pandemic enabled work to become more emergent than engineered.
How do we go about organizing work beyond the constraints of the traditional job, in a way that creates a kind of dynamic stability that unleashes the potential of both organizations and people at scale and speed?
To move beyond the industrialization of work and jobs, organizations are generally moving in two directions. In one direction, organizations seek to atomize the work and the worker—deconstructing both into their component parts (tasks or projects; skills and capabilities), and then using new advances in technology to rapidly match the “pieces” of work and worker based on evolving needs and interests. The other direction seeks to organize work by creating very broad commitments to problems to be solved, outcomes to be achieved or new sources of value to be created, essentially providing guardrails for workers in terms of the broad “what” of work—but giving them the freedom and autonomy to choose the “how” (see Figure 1).
Fractionalizing work into component tasks can lend itself to farming out work to gig or other off-balance-sheet workers—thereby undermining the stability, purpose, opportunities for growth and stable income achieved through employment that most workers desire. For this reason, we do not discuss gig economy options in this article, preferring to look at how organizations can create stable homes for workers as employees, and as part of their commitment to stakeholder capitalism, while still empowering them with the autonomy, agency and choice that many enjoy as gig workers.
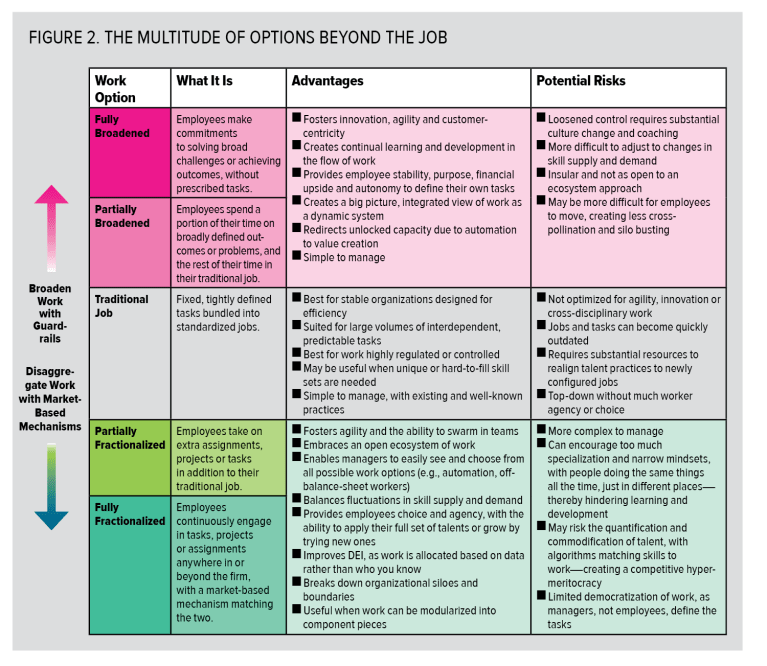
In reality, these are two ends of a fluid spectrum of options, with many alternatives in between. Organizations will want to use different options for different workforces or businesses. Indeed, there is still a place for traditional jobs in most organizations but that should be perceived as one of many options for organizations (see Figure 2).
Fractionalize Work and the Workforce
Unbundling work from the job and dividing it into component pieces unleashes people’s ability to swarm—to dynamically flow to the work by taking on short-term challenges, opportunities, tasks, projects or assignments that span job titles and departments. Unboxing people from jobs and deconstructing them into their full range of skills, experience and interests enables them to be seen as unique individuals beyond their job descriptions, with significant diversity, inclusion and equity implications.
New technology developed by companies such as Eightfold.ai, Gloat and Hitch enable employees to have visibility into projects and assignments anywhere in an organization, and suggest and match potential opportunities based on interests, availability and AI-inferred skills. This is partial fractionalization—where employees maintain their standard job, but can also take on additional work elsewhere as needed or desired.
Using such a project marketplace, employees at Tata Communications contribute to a project in addition to their core job responsibilities. HERE Technologies allows employees to carve out time from their core job responsibilities (e.g., 5 percent, 20 percent, sometimes 100 percent) for the duration of the project or task, negotiated between managers. Former HERE CHRO and founder of Hitch.works, Kelley Steven-Waiss, calls this the principle of “You get what you give;” you give the time of your employees to others, but you also get the ability to leverage talent from elsewhere in the organization.1
Consulting firms work in large part like this today, as do internal, project-based consulting groups or data-science teams who are “rented” out to other functions in the firm. At Haier, the entire organization of over 75,000 employees works in a fully fractionalized model, with an internal talent market that governs the deployment of talent focused on specific projects. The core organizational units are self-organizing, fluid microenterprises (MEs), each with 10-15 employees. All talent can join, start or move to a microenterprise at will. MEs are grouped into platforms, responsible for getting ME teams together and helping identify opportunities for collaboration. There are only three categories of employees—the platform owner, the microenterprise owner and the entrepreneur—with no higher or lower rank.2
Haier also enables internal and external entrepreneurs (employees and independent contractors) to join MEs and platforms.3 We are seeing signs of convergence of types of talent marketplaces—internal talent marketplaces; external gig marketplaces; the cross-company talent exchanges that emerged in the pandemic; and even internal talent marketplaces that connect with one another.
Fractionalizing work is very useful in a fast-changing work environment, but it can risk over-indexing on skills, the quantification of people and specialization—ultimately risking its goal of humanizing work entirely. Managers may only want to engage with employees who already have the proven skills they need, for example, sacrificing employee development.
It may also lead to what Tom Malone predicted back in 2011 as the dawning age of “hyperspecialization,” in which work previously done by one person is divided into more specialized pieces done by multiple people, achieving improvements in quality, speed and cost.4 The danger? People can become too specialized in specific skill areas, lack the incentive to grow and develop in new ways, or have little scope to improvise or add more value. Slicing work too thin can turn “that’s not my job” into “that’s not my task,” and prevent people from having the big-picture view that enables them to spot opportunities that will reinvent the future.
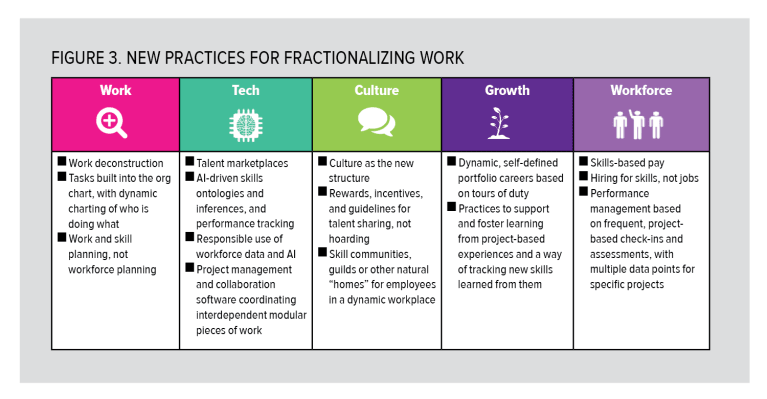
With the right decision frameworks, culture and guidelines, organizations can avoid such risks and accelerate workforce resilience, agility and capability, and impact the future of work.5 Indeed, fractionalization is more of a wholesale operating model reinvention than it is a technology play, demanding an entirely new set of work, talent and management practices to support it (see Figure 3).
Broaden Work and the Workforce
Instead of atomizing jobs into pieces, an alternative is to broaden them so that the focus is on the broad outcomes to be achieved or problems to be solved. With latitude in defining the “how” of work in pursuit of broad objectives, employees get the opportunity to take on bigger, more integrated roles and responsibilities that often cross functional boundaries and enable them to develop new skills and gain experience.
For decades, businesses have gradually embraced worker empowerment, with the move to DevOps, agile, intrapreneurship, teams of teams with distributed control and centralized coordination, self-management, edge-centric decision making, and “teal organizations” all signaling a direction away from rigid jobs. Many organizations have broadened roles for limited periods of time—Hackathons, IdeaJams and Google’s famous “20 percent time” for engineers to spend time on any project they feel will most benefit the company are examples. So too is LinkedIn’s “InDays,” in which employees are given a day a month to focus on something they are passionate about or that inspires them.6 But too often, organizations simply bolt these approaches onto legacy jobs and expectations.
A few organizations are fully embracing broadened roles—either at the individual or team level. Consider tomato processor Morning Star, where no one has a job title. Instead, each employee drafts their own outcomes and problems to be solved. For example, one worker’s personal mission is to turn tomatoes into juice in a way that is highly efficient and environmentally responsible.
The statement then describes how they will work to achieve the objectives—including whom they collaborate with and what decision rights they have—which is then approved by co-workers. Only two management layers exist: the president, who makes strategic decisions, and everyone else. But the organization isn’t flat; authority (and pay) is based on expertise and value created rather than positional power.
“We believe you should do what you’re good at, so we don’t try to fit people into a job,” says Paul Green Jr., who led the company’s training and development efforts. “As a result, our people have broader and more complicated roles than elsewhere.”7 Employees are also held accountable by their peers. Several compensation committees, each composed of peers and elected by peers, work to validate self-assessments.
To help employees spot new opportunities and think like owners, Morning Star makes all financial data transparent to employees and invests in education that ensures employees understand not only their costs, but also the value that they’re creating. Results are impressive; Morning Star has grown its volume, revenue and profit by double-digit percentages annually for the past two decades.8
ING Netherlands, in contrast, defines work around team outcomes rather than individual ones. The organization’s organizational building block is multidisciplinary teams or squads—comprised of a mix of marketing specialists, product and commercial specialists, user-experience designers, data analysts, and IT engineers—all focused on a shared outcome.
Similar to Morning Star, each squad has to write down the purpose of what it is working on, agree on a way of measuring the impact and decide on how to manage its daily activities. Squads are part of 13 tribes that address specific domains, such as mortgage services, securities and private banking. Tribes meet quarterly to celebrate and learn from successes and failures and align with the overall strategy and other tribes and squads. Chapters coordinate members of the same discipline—data analytics, say, or systems processes—who are scattered among squads.
To support the new model, ING introduced a new performance-management program emphasizing ongoing feedback, alignment of individual and organizational purpose, self-defined targets based on contributions to the team, and personal “stretch ambitions” to ensure innovation over incremental improvements. Broadened jobs meant that ING reduced the number of job types from approximately 85 to 15, including retiring the traditional full-time manager role. HR Director Maarten van Beek explains, “I strongly believe that, in future organizations, we need to match people’s skills with the jobs that need to be done. We have to move away from functions, fixed jobs and function houses.”9
The opportunity to shed the notion of the job as a relic of the industrial era in favor of broadly defined roles has never been greater. First, due to new advances in technology, we can arm every employee with the data and insights to make smart decisions. The advent of human-machine collaboration means that work processes can become far more iterative in a test-and-learn cycle of work. As technology increasingly automates routine tasks, it frees people to apply their capabilities to creative problem-solving.
Even though advances in tech are making it easier to successfully broaden roles, there is a counter-trend on the rise: using automation and AI to more tightly control how people do their jobs and tasks that takes Tayloresque tracking and control to radical new heights. Companies are now using AI to do everything from tracking and guiding a warehouse worker’s hand movements to directing truck drivers’ routes and schedules to providing differing call-center scripts based on AI-categorized customer issues. Instead, companies should consider using AI to empower workers to make better decisions on their own and spot new opportunities.
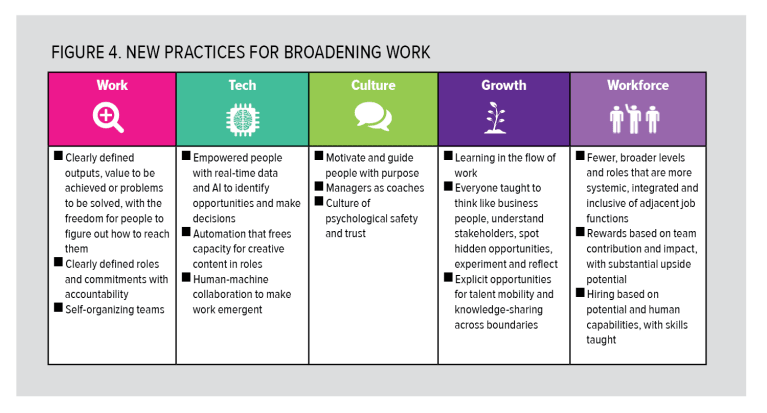
Although broadening work grants more autonomy to employees, the trade-off is abandonment of the idea that there is one best way to do things. Instead, control is achieved through the clear articulation of broad outcomes, mutual accountability, transparent information sharing, and strong cultural principles, values and norms fostered through longer employee tenures. Rewards based on shared outcomes incent employees to creatively generate more value, but intrinsic motivation achieved through aligning work with purpose and passion is the real driver of performance (see Figure 4).
It can also take quite a bit of coaching, cultural change and hard work to engage employees in solving unanticipated problems and freely working toward outcomes. Many people prefer to think in terms of tangible, narrow rules and pre-defined tasks and may be less comfortable with work that continually evolves based on specific contexts and challenges.
To transition, organizations can gradually expand the scope of the broadened role, start employees with pre-defined problems, and start providing the data, tools and AI support to help employees make more of their own decisions. AI can even be used to help; Klick Health’s Genome machine-learning technology, for example, analyzes every project at every stage in the firm, rewarding more responsibility to people who have demonstrated consistent competency and success.10
Compared to fractionalization, broadening work focuses more on non-routine tasks and emergent work rather than tasks and projects predefined by managers, boosting an organization’s “surface area” to innovate and adapt. Workers never fall into the trap of “that’s not my task or project.” But it may also be more difficult for employees to fluidly move around the organization, thereby making it harder to cross-pollinate ideas or smooth out differences in skill supply and demand.
Unlike fractionalization, the focus is less on specific hard skills and more on broad human capabilities like problem solving, curiosity and creativity necessary to identify problems and opportunities and then develop, test and iterate on solutions. Specific skills tend to be learned on the job and grow over time in the flow of work itself. Although people may not have the opportunity to use their full range of skills as they might with a fractionalized approach, neither do they risk being treated as fungible skills in a competitive marketplace. Instead of seeing the world as fractured but interchangeable parts to be configured and reconfigured at will, work and people are viewed more as dynamic systems.
Tiptoeing into the Future of Work
Moving beyond the job as the primary organizing construct for work is an audacious, bold undertaking requiring a whole scale change in what it means to work, how we support it and how we fundamentally view workers—and one that will upend the very structures and mindsets we’ve become habituated to since the dawn of the Second Industrial Revolution.
But jobs as we know them are a product of their time; a rigid solution that no longer serves today’s dynamic, more complex problems. We need entirely new approaches to mobilizing and coordinating human effort—moving from people boxed into jobs to roles built around the individual; from mechanistic to organic structures; and from workers viewed as “resources” or “capital” to workers as whole, complex contributors filled with potential.
Although it might be a daunting proposition to think about doing away with jobs entirely, you can tiptoe your way into the future of work. Start inching out by experimenting with a hybrid option close to the traditional job. Then pick your spot to experiment, focusing on where the organization might have challenges or pain points, where automation is freeing up extra capacity, or where change is happening so fast that talent practices can’t keep pace. Use it to build momentum and credibility so that more people are drawn to it, joining the rising tide of work gradually becoming uncoupled from jobs. Over time, gradually seek to further fractionalize or broaden work and try out different approaches for different types of work or workforces. Ultimately, this will transform the organization so that it encompasses a variety of ways to organize work that include but go beyond “the job,” unleashing agility and unprecedented value for employees.
 | Susan Cantrell is Vice President of Products, Workforce Strategies, at Deloitte. |
References
An organization run by AI is not a futuristic concept. Such technology is already a part of many workplaces and will continue to shape the labor market and HR. Here's how employers and employees can successfully manage generative AI and other AI-powered systems.



